Estimate the Car's Velocity at 2.0 S.
Explain how you could use the graph to show that the scooters acceleration is constant during the intervals 1020 s and 5060 s. Give your answer in SI units.
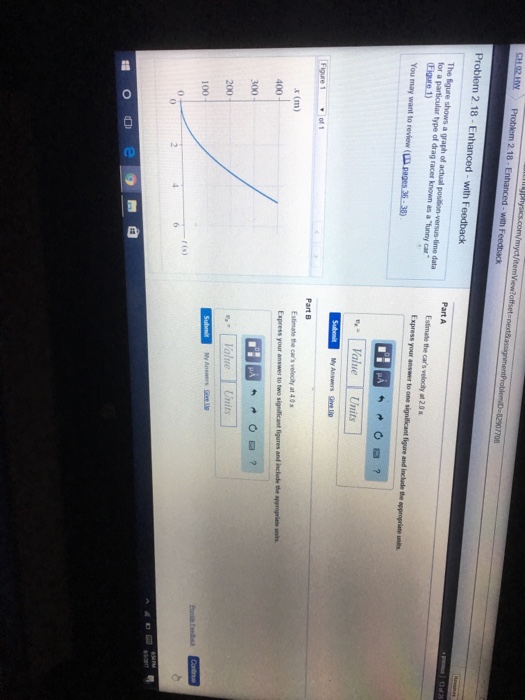
Solved The Figure Shows A Graph Of Actual Chegg Com
Since the initial velocity was zero the final velocity is equal to the change of speed.
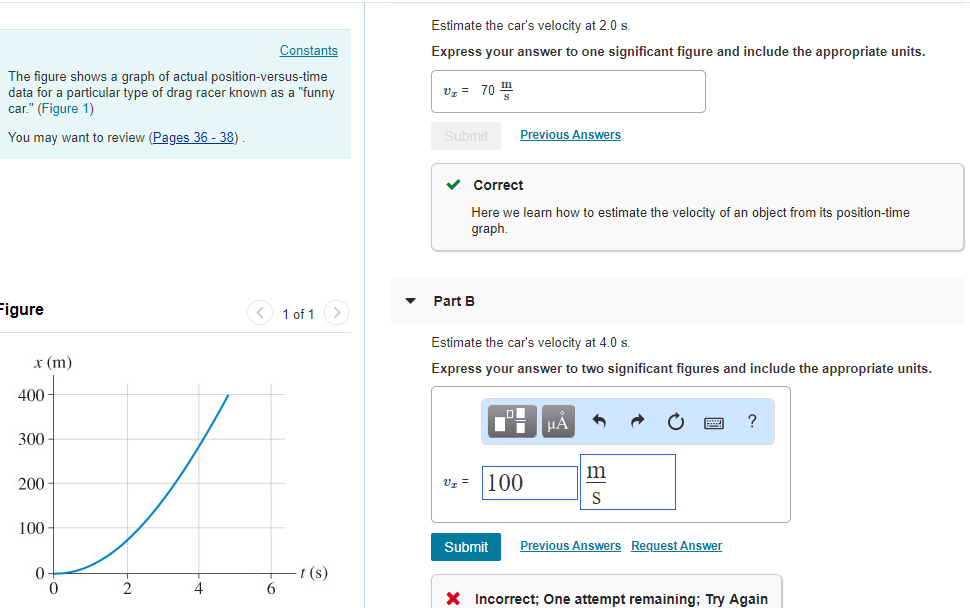
. Estimate the cars velocity at 40 mathrms Answer. Calculate the work done to attain a car of velocity 30ms having mass 100kg. 47 48 51 The diagram below shows a baseball being hit with a bat.
A car with a velocity of 30 ms accelerates uniformly at the rate of 20 ms2 for 10 s. Draw a smooth curve through the points on your graph then use your graph to estimate the cars acceleration at 20 mathrms and. A car travelling with a velocity of 20 ms E accelerates at 05 ms2 E for 100 seconds.
278 36 100 kmh. Ts Vmph 0 0 2 28 4 46 6 60 8 70 10 78 b Draw a smooth curve through the points on your graph then use your graph to estimate the cars acceleration at 20 s and 80 s. A car starts from rest and travels for 50 s with a uniform acceleration of 25 ms2.
Ms2 C 50 ms2 D 10. 66 metres to the right. I already know that the.
20 s D 45 s. Estimate the cars velocity at 20 mathrms text b. Ravi9848267328 ravi9848267328 kineric energy12mv2 051003030 45000.
___ 13 The speed of a car is decreased uniformly from 30. The car accelerates at 20ms2 for 40 s and then maintains this new velocity. Meters per second in 40 seconds.
An estimate of the derivative can be made by the central difference formula namely. If the brakes are applied for 20 s how fast is the. A motorized scooter starts from rest and accelerates for 4 s at 2 ms2.
The position of the front bumper of a test car under microprocessor control is given by x t217m 480ms2t2 0100ms6t6. F 02 18-00 20245 fs². It continues at a constant speed for 6 s.
Calculate the concentration of nicotinic acid HNic nicotinate Nic- and hydrogen ion H in a solution of 028. The magnitude of the cars acceleration is A 40. Based on your graph is the acceleration constant.
Make a graph of velocity versus time. Calculate the distance traveled. What is its final velocity.
Calculate the average velocity of the car over the time. A car accelerates from rest at a rate of 4 m s 2 for 10 s. We can use the equation s v_0t 12at2.
0 12345678 91011 12 Time seconds. Calculate the speed of the car at the end of 10s. S 50 ms60s 1220ms260s2 s 300 360 m s 66 m This means 66 metres to the right will be the.
Meters per second to 10. Compared to the magnitude of the cars total displacement the distance. Graph the scooters velocity versus time.
Up to 256 cash back a Convert the velocities to ms then make a graph of velocity versus time. A car accelerates uniformly so that it goes from a velocity of 2 0 m s to a. Graph the velocity of a car accelerating at a uniform rate from 70 ms to 120 ms in 20 s.
Remember that acceleration is the slope of the velocity. This is your average speed. This means that our final answer for displacement will be positive as well.
And 110 miles divided by 20 hours is 55 miles per hour. During which interval is the scooters average acceleration greater 1020 s or 5060 s. The velocity of a car increases from 20 ms to 160 ms in a time period of 35 s.
To calculate the average speed over the whole trip you look at the whole distance traveled which is 80 30 110 miles not just 85 miles. The graph below represents the velocity -time relationship for a 20-kilogram moving along a horizontal frictionless surface. - 9247302 abhigenius2992 abhigenius2992 09042019 Physics Secondary School answered Calculate the work done to attain a car of velocity 30ms having mass 100kg.
Use the graph you made in 13. Ms2 ___ 14 The diagram below represents the relationship between velocity and time of travel for four cars A B C and D in straight-line. Calculate the accerleration - 8912422.
The acceleration is not uniform as evidenced by the fourth column which is an indication of the acceleration decreasing. First it asked me to calculate the distance during. Velocity change 695 4 278 ms.
The changing velocity of a car is represented in the velocity-versus-time gr 0234 a In Fig. Find its acceleration the second instant when the car has zero velocity. And this is a position of 104 meters.
We start by noting that all the motion given is moving to the right or in the positive direction. The driver then applies the brakes causing a uniform negative acceleration of -30 ms2. Graph the scooters velocity versus time.
Unless otherwise noted use g 1 0 m s 2 and neglect air resistance A. A car with a velocity of 30 ms accelerates uniformly at the rate of 20 ms2 for 10 s. So in part C plugging in the numbers we get 115 meters as the position and the speed is 3 meters per second.
You can convert units to kmh by multiplying the result by 36. Explain how you could use the graph to show that the scooters acceleration is constant during the intervals 10-20 s and 50-60 s. And then for Part D we have all the quantities for part D here.
211 what is the. Calculus - average velocity VELOCITY OF A CAR Suppose the distance s in feet covered by a car moving along a straight road after t sec is given by the function s ft 2t2 48t. Multiply the acceleration by time to obtain the velocity change.
The time being 20 seconds and otherwise initial velocity and acceleration being as the same as for the other parts of the question. F t f th-f t-h2h ε O h² When t02 we get.
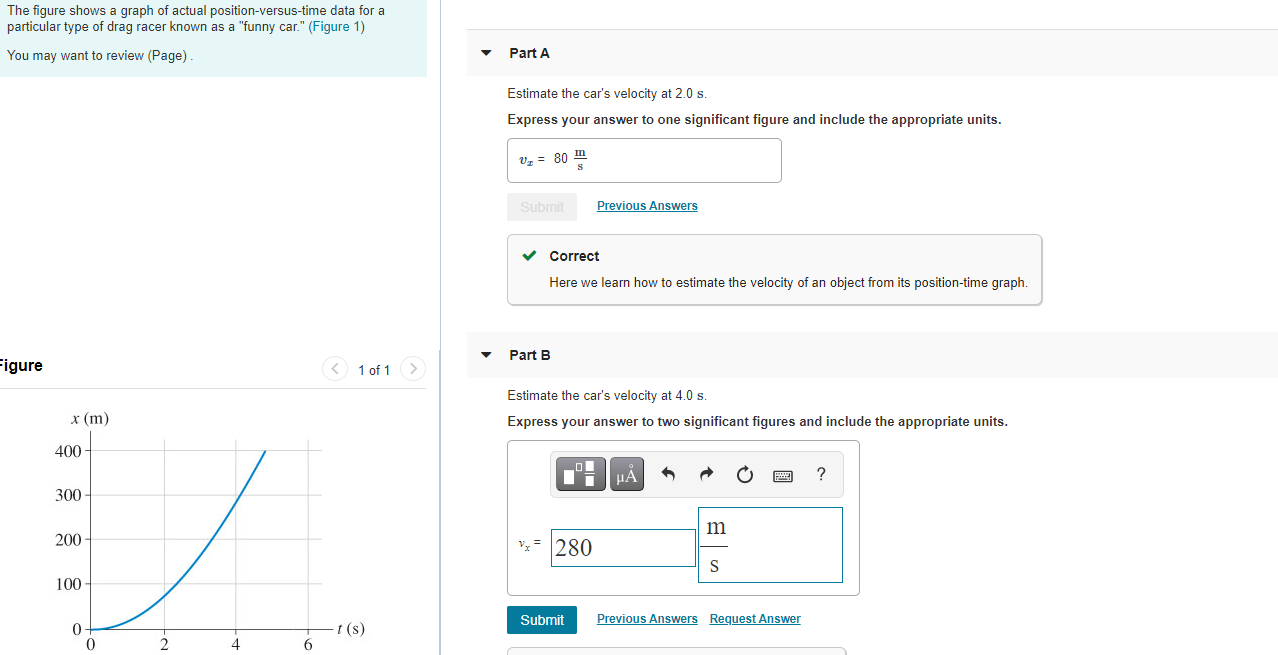
Solved The Figure Shows A Graph Of Actual Chegg Com

Solved Estimate The Car S Velocity At 2 0 S Express Your Chegg Com
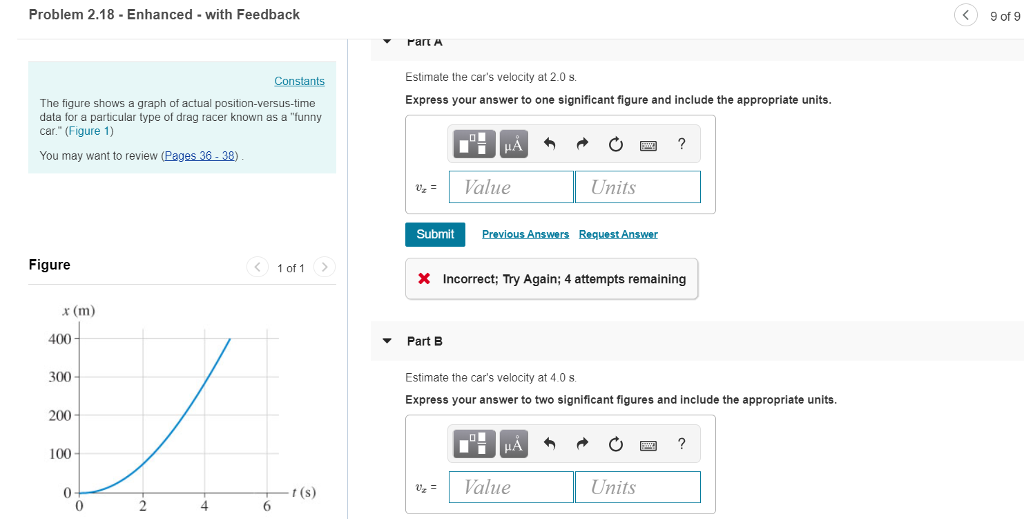
Solved Problem 2 18 Enhanced With Feedback 9 Of 9 Art A Chegg Com
No comments for "Estimate the Car's Velocity at 2.0 S."
Post a Comment